Configuring SAML authentication for Azure Active Directory on Hue
— SAML, Active Directory, Hue, Hadoop — 3 min read
Introduction
I recently had to undertake the task of deploying a new Hue container with SAML authentication. In reaching a working solution I found myself troubleshooting more than initially anticipated, in part due to gaps in Hue's documentation and an apparent bug in one of its underlying dependency packages.
My goal in publishing this article is to provide a concise resource for others who are also integrating Hue with Azure Active Directory (AD). In writing this I'm making the presumption that the majority of readers will have searched the internet for this specific topic and already have a baseline understanding of Hue and AD. Accordingly, in the interest of brevity, some foundational topics aren't discussed in detail but rather referenced through the inclusion of hyperlinks to external resources.
One final disclaimer is that the solution discussed here is based upon my experience of the latest open-source release, Hue version 4.10.0. If you are using a future release and/or Cloudera's enterprise version, some syntax/features may differ.
Choosing a SAML claim
The following diagram sourced from Azure AD's documentation outlines the flow through which users of your web app are authenticated against your Active Directory and SAML tokens are returned.
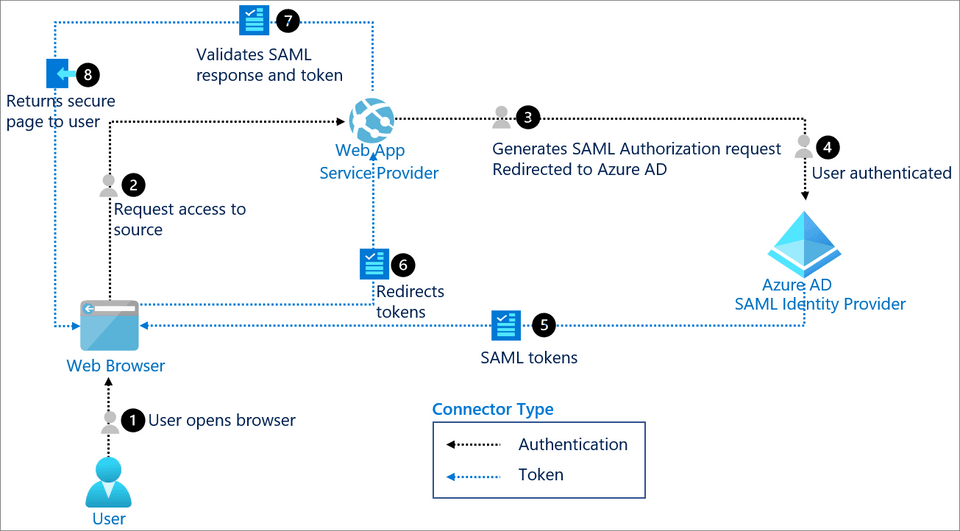
These SAML tokens contain claims (ie. user name, email address etc.) that are used by Hue when each new user logs in for the first time.
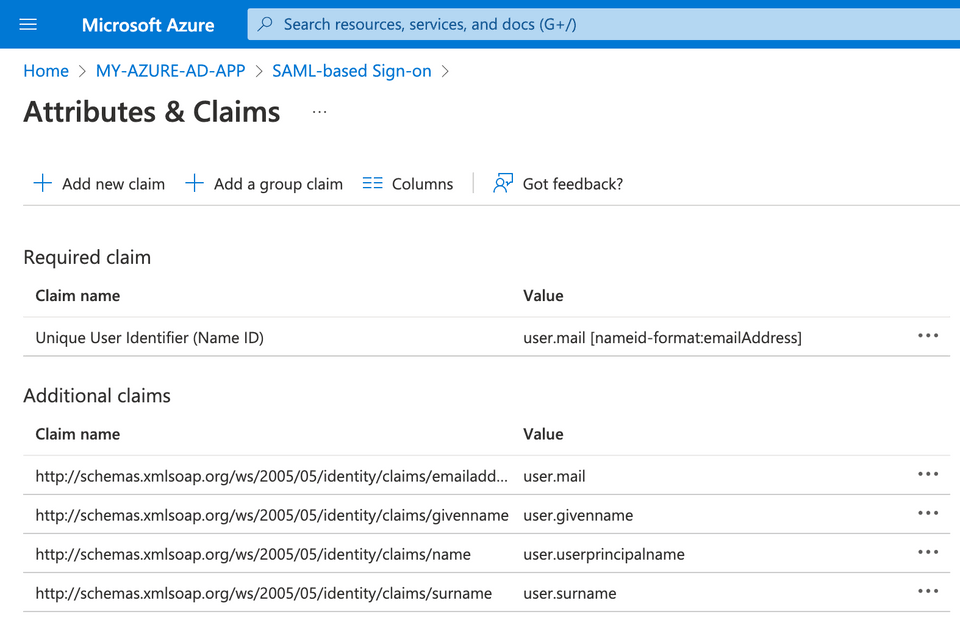
Within your Azure AD console, you will see these claims listed for your current app (if you have not already created a new application in Azure AD, here's a good tutorial from Microsoft's documentation).
When searching Google for guidance on SAML configuration in Hue, two of the most prominent and relevant resources are this blog post and this discussion on the Cloudera forum, both of which direct the user towards an 'attribute mapping' approach. This approach involves creating a configuration file that enables Hue to map our SAML claims to internal variables that it then uses to populate its database. Unfortunately, there appears to be a bug in the current open-source release of Hue(v4.10.0) which results in this mapping approach failing.
With this context in mind, I found the simplest option to be an alternative solution which is briefly referenced in the previously-linked Cloudera forum discussion.
As opposed to the other AD claims, Unique User Identifier (Name ID) is ingested by Hue without the need for any custom mapping. This results in the following hue.ini configuration:
1username_source=nameid2name_id_format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress"We will return to the hue.ini configuration in more detail later, but for now let's focus on the name_id_format value.
Deeper context and specific formatting references can be found in the Azure AD documentation, but at a high level, there are four possible formats that we can choose to configure:
emailAddressreturns the NameID claim in e-mail address formatpersistentreturns the NameID claim as a pairwise identifier, a randomly-generated value. This is created once and the same value is returned every subsequent time.transientreturns the NameID claim as a randomly generated value. A new value is generated each time a user logs in.unspecifieddictates that your identity provider will determine the claim format that is returned. In Azure AD's case this means that a pairwise identifier is returned.
As the other formatting options return randomly-generated values, emailAddress is the obvious choice if we want the ability to easily identify users in the Hue admin console.
Generating SSL keys
In order for our Service Provider (Hue) and Identity Provider (Azure AD) to communicate securely, we must configure an SSL certificate and private key.
Azure AD automatically creates a certificate for new apps, but as the corresponding private key is not made available to us and Hue requires this, we will need to create a new key/cert and upload to Azure AD.
Specifically, Azure AD requires a .pfx filetype and rsa encryption while Hue requires .PEM files with a X.509 certificate.
With these requirements in mind, we can create the .pem key and cert files before converting to .pfx and uploading to Azure AD.
1openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -keyout hue_key.pem -out hue_crt.pem -days 3652openssl pkcs12 -inkey hue_key.pem -in hue_crt.pem -export -out hue.pfxThe second of these commands will prompt you for a password. Make note of your chosen password as you will need it when uploading the .pfx file to Azure AD.
For a granular reference on openssl, see the openssl documentation or pass the --help option in your command line (eg openssl req --help).
With our hue.pfx file created we can now upload it to Azure AD and download the Identity Provider metadata file that Azure will auto-generate.
Within the Azure AD console, you should see a similar layout to this:
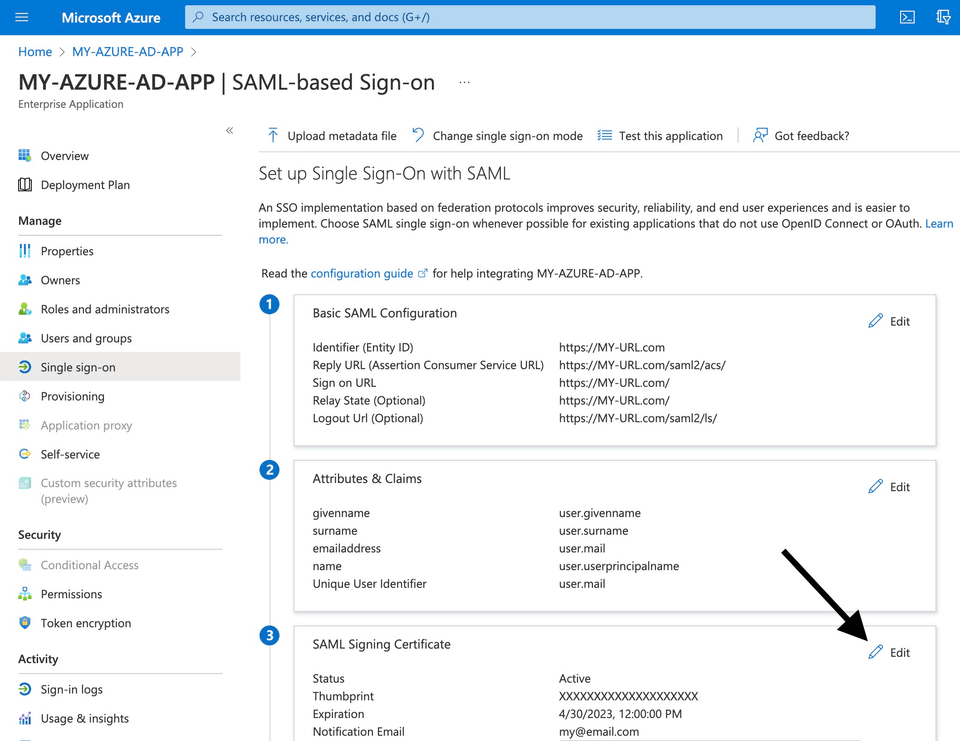
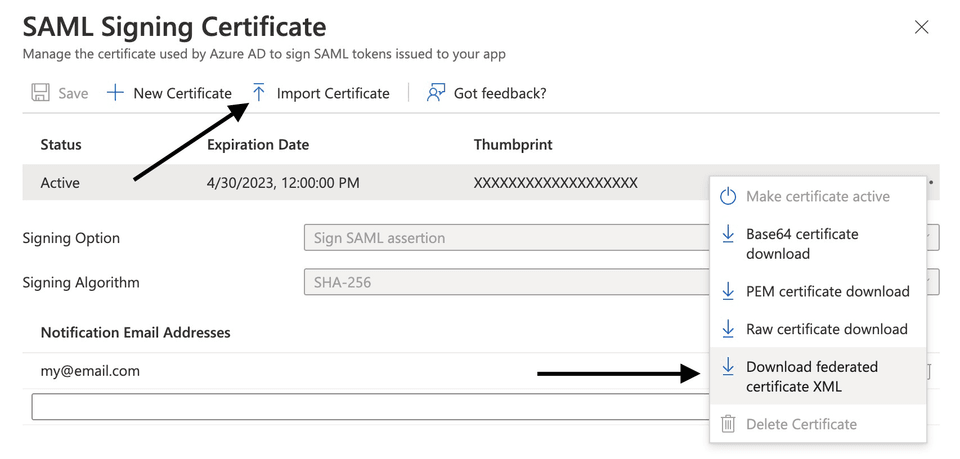
If you edit the SAML Signing Certificate section, you will see options to import a .pfx certificate and download a 'federated' XML file for the certificate that you have just uploaded.
Configuring Hue
For setting the configuration, your hue.ini file should contain the following keys:
1[desktop]2 redirect_whitelist=^\/.$,https:\/\/login.microsoftonline.com\/YOUR-UNIQUE-URL-SLUG\/.*$3
4 [[auth]]5 backend=libsaml.backend.SAML2Backend6
7[libsaml]8 xmlsec_binary=/usr/bin/xmlsec19 metadata_file=/opt/cloudera/security/saml/azure-ad-metadata.xml10 key_file=/opt/cloudera/security/saml/my_key.pem11 cert_file=/opt/cloudera/security/saml/my_cert.pem12 entity_id=https://MY-URL.com13 username_source=nameid14 name_id_format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress"Hue's documentation is a useful reference for most configuration settings. As this documentation is not entirely thorough, referencing hue.ini in Hue's source code will give deeper insights with additional comments that are not reflected in the documentation.
Uploading Hue metadata to Azure AD
Our final step is to upload Hue's metadata .xml file to Azure AD.
Upon starting Hue, a metadata file will be viewable at https://MY-URL.com/saml2/metadata/.
After downloading a copy of this file, you can upload to Azure AD via its Upload metadata file button.
Once this metadata file is uploaded, you will now be set to authenticate Active Directory users on Hue via Single Sign On.